Boeing Strike Extended as Machinists Snub New Labor Contract!
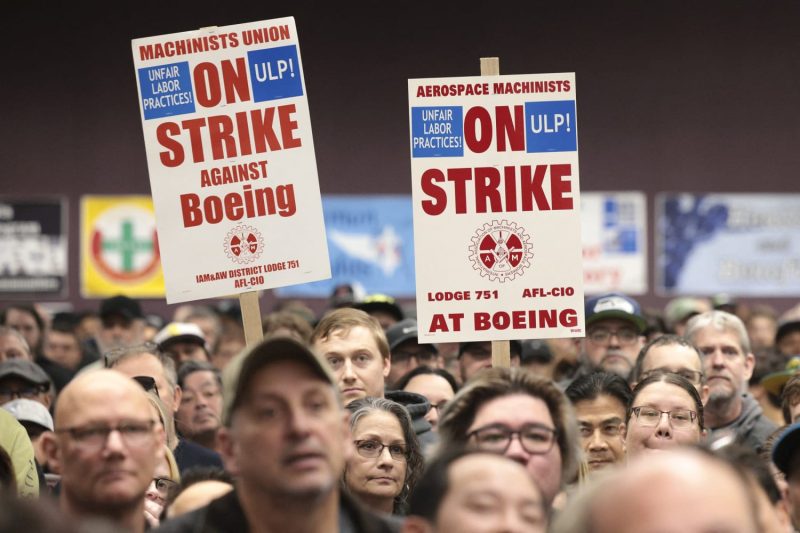
Boeing, the renowned American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, and missiles worldwide, witnessed a significant turning point recently. The company’s machinists, affiliated with the International Association of Machinists and Aerospace Workers (IAM), rejected a fresh labor contract, continuing to extend an ongoing strike action.
One of the most influential workforces in the industry, the machinists play a crucial role in the day-to-day operations of the company. This rejection of the proposed contract is not only unfortunate, but it also signifies a labor dispute that may significantly hinder the production volume of the company.
The discontent stemmed primarily from the provisions of the new contract that the machinists considered unfavorable. These included changes in their retirement benefits, healthcare plans, wage structures, and job security. On the issue of retirement plans, the proposed contract aimed to transition from the traditional pension plan to the 401(k)-style retirement savings plan. A move that the machinists believed would diminish their financial security in the long run.
The healthcare change also posed a notable issue. The machinists were alarmed by the significant increase in their out-of-pocket health costs under the new contract. They anticipated this would considerably eat into their take-home pay. Coupled with this, the proposed wage structure didn’t promise substantial increments that the workforce considered proportional to their contributions and the company’s success.
Extending beyond financial concerns, machinists also perceived a threat to their job security through the company’s expanded power to subcontract work. Job security, essentially the backbone of any workforce’s trust in their employer, seemed under threat, fanning the flames of the dispute.
The Boeing machinists’ strike has had profound implications for the company and the aerospace industry at large. With the already slowed production due to the strike, Boeing could face delayed deliveries, causing a ripple effect throughout the aviation industry. Additionally, the company’s competitiveness may be affected as rival manufacturers could seize the opportunity to accelerate their production and gain a larger market share.
Moreover, the labor strife also casts a shadow over Boeing’s internal dynamics, employee morale, and public image. The company’s leadership may need to reassess their strategy to overcome this labor relation hurdle. They would have to re-engage the machinists to address their grievances, regain their trust, and renegotiate contract provisions that are mutually beneficial.
In retrospect, the Boeing machinists’ rejection of the new contract isn’t a mere labor dispute. It represents the workforce’s efforts to safeguard their economic well-being and job security. On the other side of the spectrum, Boeing, as a leading player in the aerospace industry, is grappling to maintain its production efficiencies and market competitiveness amidst strike actions.
As the scenario unfolds, it would be interesting to see how Boeing successfully navigates through these challenging times while striking a balance between achieving business goals and ensuring their workforce’s welfare. It will be a critical test of their leadership and decision-making capability in dealing with one of the most classic and complex scenarios a company can face – labor disputes.